Why Stroke Survivors Face Higher Risk of Tooth Decay: Causes and Prevention
Essential Takeaways
- Stroke survivors face triple the cavity risk due to dry mouth, physical limitations, and dietary changes. However, targeted prevention strategies, including high-fluoride toothpaste, frequent dental visits, and smart oral health technologies can effectively protect against tooth decay and maintain oral health long-term.
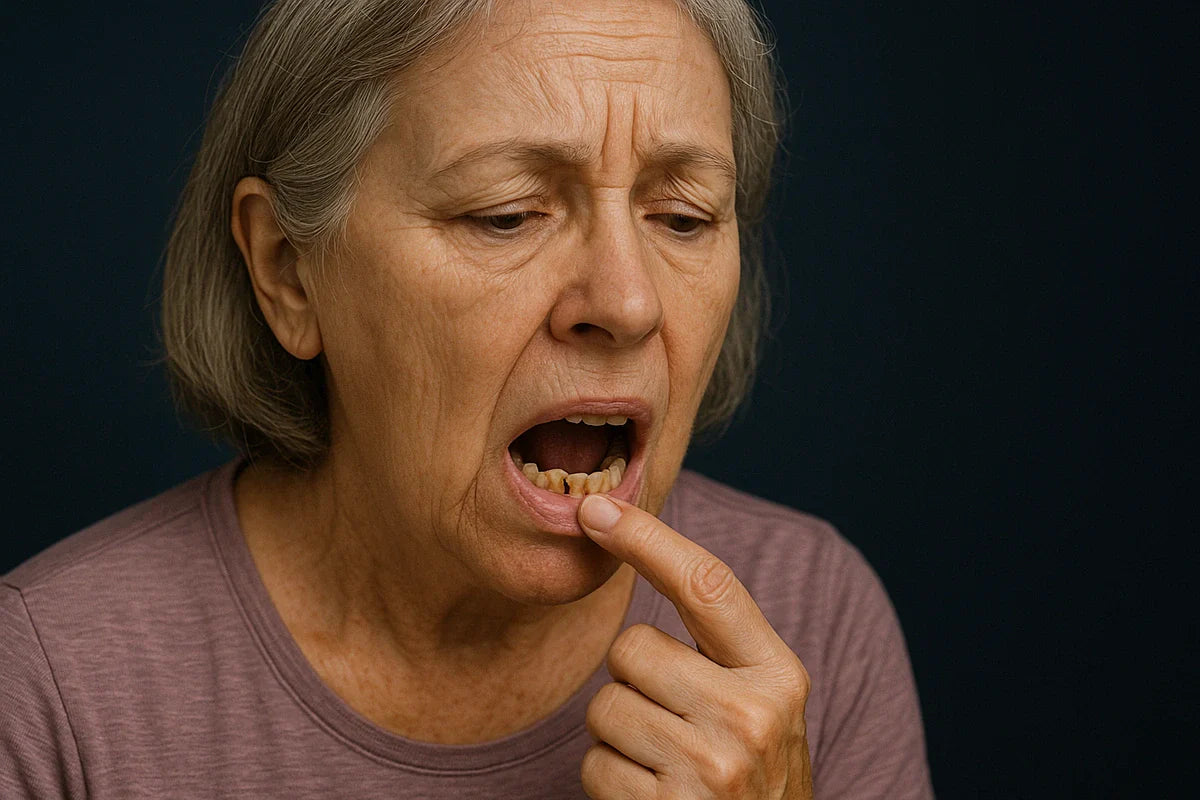
Stroke survivors experience significantly higher rates of tooth decay and oral health problems due to physical impairments, dry mouth, and dietary changes. However, with targeted prevention strategies, these dental complications can be effectively managed.
(Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2022)
The Connection Between Stroke and Dental Health
Stroke fundamentally changes how patients manage daily routines, affecting everything from saliva production to diet choices. Research consistently shows that stroke survivors develop higher rates of decayed and missing teeth compared to the general population, with poorer overall oral hygiene indices.
The impact extends beyond just brushing difficulties. Stroke affects multiple body systems that naturally protect against cavities, creating a perfect storm for dental decay.
Why Stroke Increases Cavity Risk: The Science Behind It
Xerostomia: When Dry Mouth Becomes Dangerous
Xerostomia (dry mouth) represents one of the most significant oral health challenges after stroke. Stroke can damage the nervous system pathways that control salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva flow. This matters because saliva serves as the mouth's natural defense system, neutralizing acids and washing away food particles.
Research reveals that salivary gland dysfunction and oxidative stress are commonly found in stroke survivors, directly raising their risk for cavities and gum disease. Without adequate saliva, harmful bacteria multiply more easily, and the mouth loses its ability to naturally repair early tooth damage.
Physical and Cognitive Barriers to Oral Care
Multiple clinical studies confirm that stroke survivors often lose the ability to perform regular oral hygiene, particularly those with:
- Hemiplegia or weakness affecting dominant hand function
- Cognitive impairments that disrupt routine memory
- Visual field defects making it difficult to see all areas of the mouth
- Coordination problems affecting fine motor skills needed for thorough brushing
These physical challenges mean that even motivated patients struggle to maintain the consistent oral care routines necessary for cavity prevention.
Dietary Changes That Feed Decay-Causing Bacteria
Stroke frequently causes dysphagia (swallowing difficulties), forcing patients to modify their diets significantly. Common post-stroke dietary changes include:
- Switching to softer, processed foods that stick to teeth longer
- Increasing carbohydrate intake for easier swallowing
- Consuming more fruit juices and smoothies (high in natural sugars)
- Relying on pureed foods that may contain added sugars
These dietary modifications create an environment where sugars remain in contact with teeth for extended periods, providing fuel for cavity-causing bacteria.
What the Research Shows About Stroke and Tooth Decay
Large-scale population studies consistently demonstrate that stroke patients have significantly higher rates of dental caries compared to controls. Meta-analyses of stroke survivors reveal:
- Increased decayed tooth surfaces across all age groups
- Higher rates of tooth loss within the first year post-stroke
- Worse oral hygiene scores that persist even years after initial stroke
Clinical research also confirms that stroke survivors with inconsistent oral care routines develop cavities at accelerated rates, with the most severe problems occurring in patients who depend entirely on caregivers for dental hygiene.
Evidence-Based Prevention Strategies for Stroke Survivors
Advanced Fluoride Protection
- Use high-fluoride toothpaste (1,450-5,000 ppm fluoride as prescribed by your dentist)
- Apply fluoride gel or varnish during regular dental visits
- Consider prescription fluoride rinses for high-risk patients
Saliva Stimulation and Dry Mouth Management
- Stay well-hydrated throughout the day
- Use sugar-free gum or lozenges to stimulate saliva production
- Consider artificial saliva products for severe xerostomia
- Avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes that can worsen dryness
Modified Oral Hygiene Techniques
- Rinse immediately after meals and snacks to remove food particles
- Use adaptive equipment like built-up toothbrush handles or electric toothbrushes
- Focus on thorough cleaning rather than speed quality over efficiency
- Ask caregivers for assistance when needed without embarrassment
Dietary Modifications for Oral Health
- Limit sugary beverages including fruit juices and sports drinks
- Choose water as the primary beverage between meals
- Rinse with water after consuming soft, sticky foods
- Avoid prolonged snacking that keeps sugars in contact with teeth
Advanced Technology Solutions for Stroke Survivors
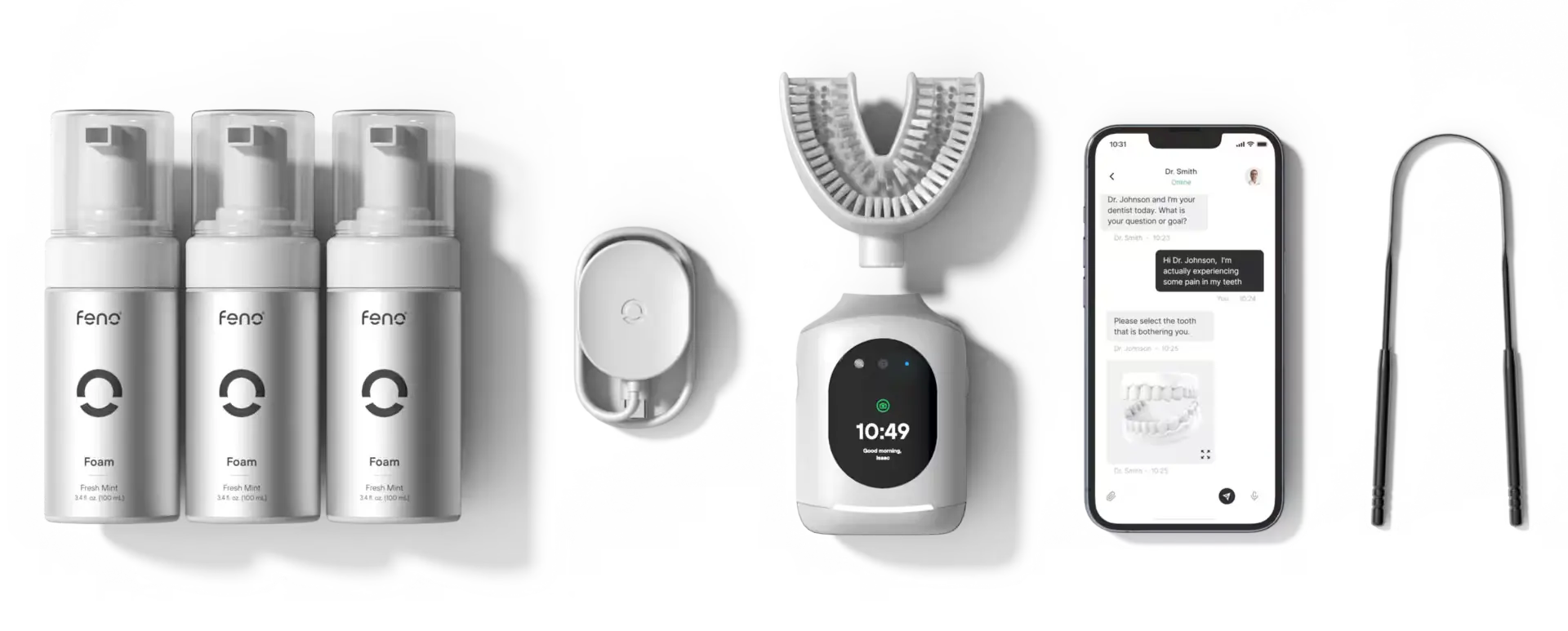
For stroke survivors struggling with traditional brushing techniques, innovative oral health technology can provide game-changing solutions. The Feno Smartbrush represents a breakthrough for patients with physical limitations, offering several advantages specifically relevant to post-stroke oral care:
Addressing Physical Limitations:
- 20-second full-mouth cleaning eliminates the need for complex hand movements and coordination
- 18,000 bristles working simultaneously provide thorough cleaning that would be impossible with traditional brushing
- Personalized mouthpiece design accommodates individual mouth shapes and limitations
- One-handed operation makes it accessible for stroke survivors with hemiplegia
Smart Health Monitoring:
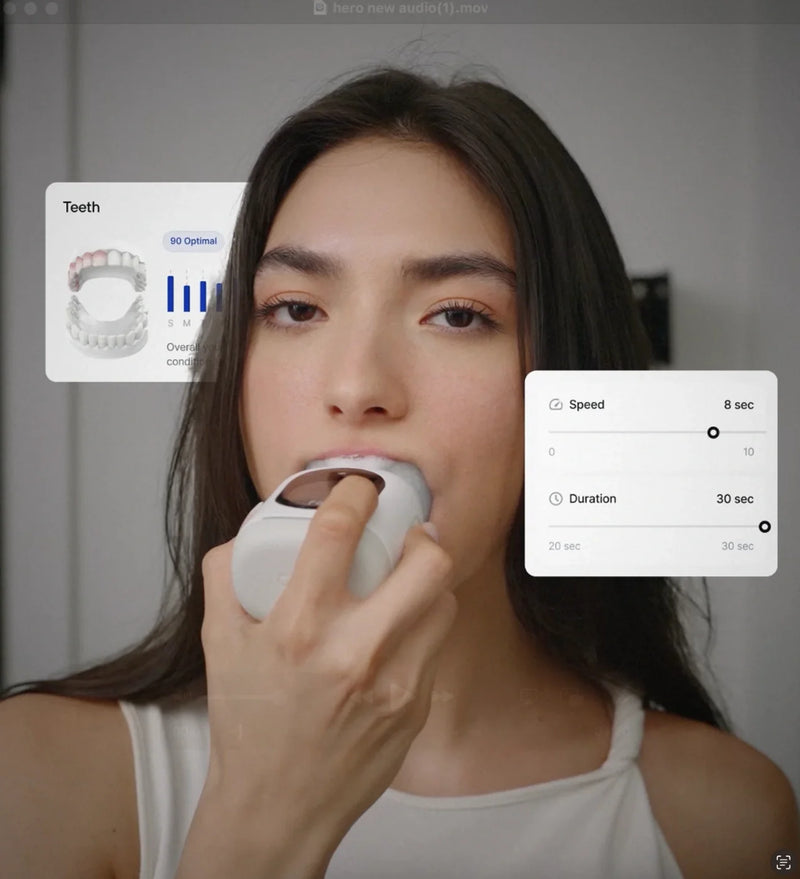
- Built-in oral scanner technology provides detailed health reports
- AI-powered app tracks oral health changes over time and identifies potential problems early
- Connected oral health coaches offer remote guidance and personalized care recommendations
- Automated plaque detection helps identify areas that need attention before they become problematic
This technology is particularly valuable for stroke survivors who may have difficulty accessing regular dental care or maintaining consistent oral hygiene routines. The comprehensive health reports can also help caregivers and healthcare providers monitor oral health status remotely.
Learn more about advanced oral health solutions at Feno.co
When to Seek Immediate Dental Care
Stroke survivors should contact their dentist immediately if they experience:
- Persistent tooth pain or sensitivity
- Swelling in the gums or face that could indicate infection
- Bleeding gums that doesn't improve with gentle cleaning
- Changes in taste or persistent bad breath
- Difficulty chewing that affects nutrition
The Path Forward: Hope and Practical Action
While stroke creates unique oral health challenges, current research demonstrates that targeted prevention strategies can successfully reduce cavity risk. The key lies in recognizing that post-stroke dental care requires a modified approach. Not abandonment of oral hygiene, but adaptation to new realities.
Success depends on three pillars: consistent daily care (even if modified), regular professional monitoring, and early intervention when problems arise. With proper support and the right tools, stroke survivors can maintain healthy teeth and gums for years to come.
Remember: Small daily efforts in oral care can prevent major dental problems later. Every stroke survivor deserves to maintain their smile and the confidence that comes with good oral health.

Feno Founders Edition Bundle
Advanced Oral Health in 20 Seconds with the Feno Smartbrush™
Get Yours Now!